Choi, Cho, Choi, Jung, and Seo: Successful Reconstruction of Bone and Soft Tissue Defect Using Artificial Dermal Matrix after Hand Injury due to Dog Bite
Abstract
Here we report a successful treatment of animal bite wound involving the bone. We used an artificial dermal matrix to reconstruct the cortical defect and prevent adhesion of the tendinous structures. A 48-year-old woman visited the emergency department for a painful hand swelling due to a dog bite 2 months earlier. A physical examination revealed a firmly palpable lesion with swelling and tenderness on the dorsal aspect of her hand. Magnetic resonance imaging found lytic changes of the second metacarpal bone with cortical destruction and fluid collection. After debridement of the necrotic tissue, a cortical bone defect with inflammatory changes of the medulla was noted. Following several days of irrigation, an artificial dermal matrix was applied with skin flap coverage to restore the soft tissue and bone defect. Three months later, the patient showed good motion of her hand without any restrictions. We believe artificial dermal matrix can be a good treatment strategy for restoring bone defect and preventing tendon adhesion simultaneously.
Key Words: Bites and stings; Osteomyelitis; Acellular dermis
서론
개에 의한 교상은 동물에 의한 교상의 대부분을 차지하고 있으며 세계적인 보건 문제 중의 하나이다[ 1]. 성인의 경우, 우수에 대한 손상이 호발하며 손상의 정도는 찰과상부터 관통상, 천파창에 이르며, 이로 인한 합병증은 감염, 개방성 골절, 힘줄 혹은 관절 손상에 이르기까지 다양하다[ 2]. 교상 치료는 손상 정도에 따라 결정되며, 일차 봉합 후 경과를 관찰하는 경우부터 입원하여 연속적인 창상 세척과 정맥항생제 정주를 필요로 하는 경우까지 다양하다. 또한, 추후 결손부위에 대한 재건이 필요한 경우도 있다[ 3]. 인공진피는 적용하기 용이하고, 수술 시간을 단축할 수 있으며, 공여부의 합병증이 없다는 장점이 있어 최근 그 사용빈도가 증가하는 추세이다[ 4]. Insuregraf (SK Bioland, Seoul, Korea)는 돼지에서 유래된 제1형 콜라겐을 이용하여 제작한 인공진피로서 전처리가 필요하지 않고, 진피 유래 성분이 풍부하여 세포 외 기질의 회복과 혈관화를 유도하는데 도움을 준다는 장점이 있다[ 5]. 이에 본원에서는 개에 물려 수상 후 발생한 우수 중수지골의 피질골 결손을 포함한 창상에 대해 연속적인 창상 세척 및 변연절제 후 Insuregraf를 적용하였으며 만족할 만한 결과를 얻어 이에 대해 보고하고자 한다. 본 연구에 대해 환자에게 연구동의서를 취득하였으며 헬싱키 선언의 원칙에 따라 수행되었다.
증례
특이 기저질환이 없는 48세 여자 환자가 우측 수부의 통증 및 부종을 주소로 본원 응급실을 내원하였다. 환자는 2달 전 개에 의해 발생한 교상으로 1차 병원에서 경구 항생제를 복용하였고, 1달 전부터는 증상이 호전과 악화를 반복하였지만, 경과 관찰하였다. 내원 15일 전부터는 증상이 급격히 악화되었다고 진술하였다. 내원 당시 시행한 신체 검사상 개방 창상은 존재하지 않았으나, 우측 수부의 제2 중수지절 관절 부위에 지름 3 cm 영역의 발적, 압통 및 요동을 보이는 병변이 관찰되었다( Fig. 1). 진단을 위해 시행한 X-ray 상에서는 두 번째 중수지골 골두 부위의 골 결손 관찰되었으며( Fig. 2), 자기공명영상에서는 피질골 골수염을 보이는 1.1 cm 크기의 부식성 병변이 관찰되었다( Fig. 3). 골수염 및 연조직염 진단 하 환자는 절개 배농 및 변연절제술을 시행하기로 하였다. 수술 소견상, 두 번째 중수지골두 피질골이 결손되어 수질골이 노출되어 있었으며 다량의 농형 분비물이 저류되어 있었다( Fig. 4). 또한 피질골 부위 인접한 두 번째 총 손가락폄근이 노출된 것이 관찰되었다. 본 창상에 대해 수술방에서 매일 창상 세척을 시행하였으며 입원 기간 동안 3세대 세팔로스포린(Ceftriaxone)과 메트로니다졸(Flagyl)을 투약하였다. 수술 시 시행한 조직검사상, 급성 염증 소견이 관찰되었고 균 배양 결과에서는 병원균이 배양되지 않았다. 8일간의 치료 후, 증상 및 감염 징후가 호전되는 양상을 보여 연부 및 골 결손 부위의 재건술을 계획하였다. 전신마취 하 변연절제를 시행하였으며 수술 소견에서도 더 이상의 감염 징후는 보이지 않았다. 이에 두 번째 중수지골두의 골 결손 부위에 Insuregraf를 충전하였으며, 주변 부위에도 Insuregraf를 적용한 뒤 국소피판술을 시행하였다( Fig. 5). 환자는 수술 시행 2일 후 별다른 합병증 없이 퇴원하였다. 환자는 입원 기간 12일 동안 정맥항생제를 정주하였으며, 퇴원 후 2주간 경구 항생제를 복용하였다. 입원 당시 시행한 혈액검사상, 총 백혈구 수는 내원 당시 10.06×10 3/μL에서 퇴원 시 7.47×10 3/μL로, C-반응단백질은 0.06 mg/L에서 0.03 mg/L로 호전되었다. 수술 1달 뒤, 외래 경유 시행한 X-ray 상에서 기존에 보였던 골 결손부위 회복된 모습을 보였다( Fig. 6). 이후 3개월간의 추적관찰 기간 동안 재발 및 합병증 없이 유지되었으며 신체 검사상 제2 중수지절 관절의 회복된 가동 범위(신전/굴전, 20°/80°)가 측정되었다( Fig. 7).
고찰
반려동물을 키우는 인구가 늘어나면서 동시에 동물에 의한 손상 또한 증가하는 추세로, 개에 의한 교상은 그 중의 80%에서 90%를 차지하며 수부를 포함한 상지에 발생하는 경우가 많다[ 6]. 대부분의 경우, 환자들은 동물에 의한 심각한 손상은 큰 개에 물리거나 크기가 큰 개방 창상이 발생한 경우에만 해당되는 것으로 생각하나, 작은 동물에 의하거나 크기가 작은 상처라도 적절하게 치료되지 않는 경우, 심부 감염 및 합병증이 나타날 수 있다[ 7]. 특히 손에 발생한 교상의 경우 힘줄이 움직이며 감염이 확장될 가능성이 있으므로 힘줄윤활막염, 연조직염 그리고 골수염이 발생할 위험이 높다. 또한 골수염의 경우 증상이 발현되기까지 2주 정도의 잠복기가 있고 배양검사에서도 절반 정도만이 병원균이 배양된다고 알려져 있기 때문에, 수상 당시 증상 및 배양 결과에서 음성을 보였다고 해도 주의 깊게 경과를 봐야 한다[ 8]. 골수염이 의심되는 경우 일반 X-ray, 골스캔, 혹은 자기공명영상을 시행해 볼 수 있으며 본 증례에서는 민감도와 특이도가 가장 높다고 알려진 자기공명영상을 시행하였다[ 9]. 동물에 의한 교상 치료는 창상 세척 및 일차 봉합 후 경구 항생제를 복용하며 경과를 관찰하는 것이 통상적 치료이나, 감염을 비롯한 합병증이 발생한 경우에는 정맥항생제 투여 및 수술적 처치가 필요하다. 인공진피는 섬유결합소, 콜라겐 및 엘라스틴을 포함하고 있어 인접 조직의 성장, 혈관신생을 촉진하는 것으로 알려져 있다[ 10]. 인공진피는 현재 다양한 분야의 재건에서 이용되고 있으며, 유방 및 연부조직, 화상, 창상뿐만 아니라 안면골 골절의 정복술 후 골 성장의 촉진제로써도 이용되고 있다[ 11]. 또한 수부 재건에 사용함으로써, 수술 후 발생할 수 있는 인대 유착 및 이로 인한 운동 저하를 방지할 수 있다고 보고된 바 있다[ 12]. 본 증례에서는 개에 의해 발생한 교상으로 인해 우측 중수지골두의 골수염 및 연부조직염이 발생하였으며, 이에 대해 수술적 절개 배농 및 항생제 투여 후 증상이 호전되었다. 본 증례에서 보고하는 인공진피 기질의 사용은, 골수염이 동반된 염증 질환의 치료 이후 필연적으로 발생하는 과섬유화, 반흔 및 구축 형성을 예방할 수 있다는 점에서 의의가 있다고 생각한다. 인공진피 기질의 사용을 통해, 본 증례에서는 피질골의 결손을 보충함과 동시에 염증으로 인해 발생하게 되는 수질골과 인대의 섬유화를 방지할 수 있었다. 환자는 추적 관찰 기간 동안 합병증이 발생하지 않았을 뿐만 아니라 반흔 및 운동에서도 만족할 만한 결과를 보였다.
Conflict of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article are reported.
Fig. 1.
Clinical photographs on the day of admission. A 3 cm-sized lesion showing redness, tenderness, and fluctuation. Frontal (A) and oblique (B) views. 
Fig. 2.
Initial hand X-ray. Arrow indicates bony defect on the head of second metacarpal bone. Frontal (A) and oblique (B) views. 
Fig. 3.
Magnetic resonance images. Lytic changes of the second metacarpal bone with cortical destruction and fluid replacement are visible (indicated by arrow). Axial (A) and coronal (B) views. 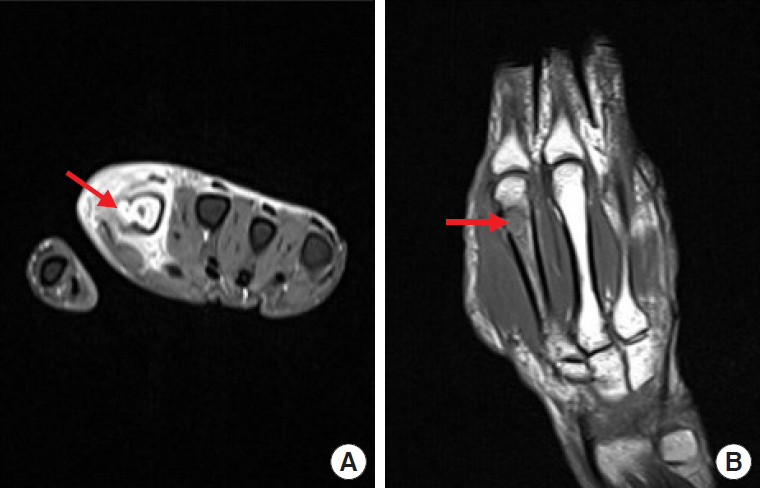
Fig. 4.
Intraoperative photograph. The defect of the 2nd metacarpal bone cortex is plain to see. 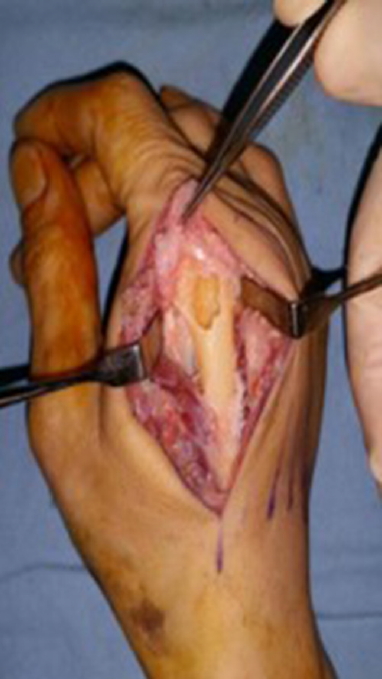
Fig. 5.
Reconstruction of bone defect with Insuregraf. 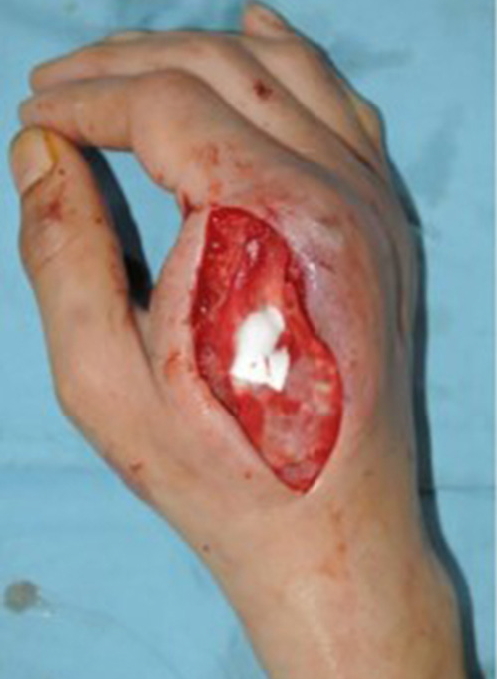
Fig. 6.
Follow-up hand X-ray after 1 month. Recovered bony defect on the head of second metacarpal bone (indicated by arrow). Frontal (A) and oblique (B) views. 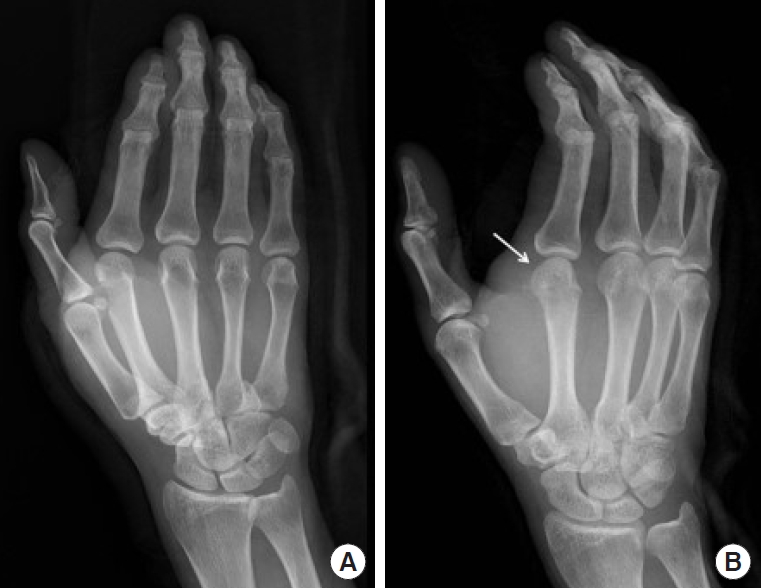
Fig. 7.
Three months follow-up photographs. (A, B) Satisfying results without any restriction of motion. 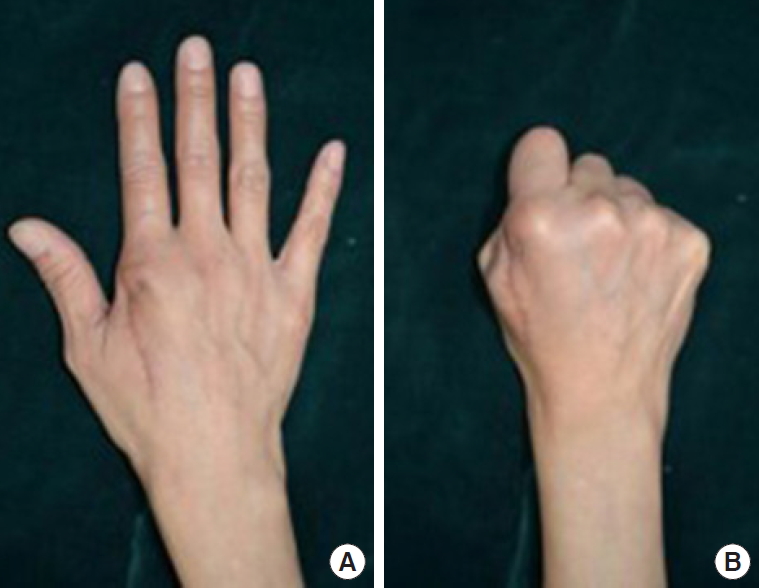
References
1. Borud LJ, Friedman DW. Dog bites in New York City. Plast Reconstr Surg 2000;106:987-90.   2. Hutson HR, Anglin D, Pineda GV, et al. Law enforcement K-9 dog bites: injuries, complications, and trends. Ann Emerg Med 1997;29:637-42.   3. Aziz H, Rhee P, Pandit V, et al. The current concepts in management of animal (dog, cat, snake, scorpion) and human bite wounds. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2015;78:641-8.   4. Ye WM, Zhu HG, Zheng JW, et al. Use of allogenic acellular dermal matrix in prevention of Frey’s syndrome after parotidectomy. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2008;46:649-52.  6. Kim SH, You JY, Ryu JY. A comparison of characteristics in dog bite patients. J Korean Soc Traumatol 2005;18:135-40.
7. Benson LS, Edwards SL, Schiff AP, et al. Dog and cat bites to the hand: treatment and cost assessment. J Hand Surg Am 2006;31:468-73.   8. Presutti RJ. Prevention and treatment of dog bites. Am Fam Physician 2001;63:1567-72.  10. Kirsner RS, Bohn G, Driver VR, et al. Human acellular dermal wound matrix: evidence and experience. Int Wound J 2015;12:646-54.   11. Kim J, Lew DH, Roh TS, et al. Use of acellular allogenic dermal matrix (MegaDerm) in orbital wall reconstruction: a comparison with absorbable mesh plate and porous polyethylene. J Craniofac Surg 2017;28:e644-9.   12. Bhavsar D, Tenenhaus M. The use of acellular dermal matrix for coverage of exposed joint and extensor mechanism in thermally injured patients with few options. Eplasty 2008;8:e33.  
|
|