Diagnosis of Systemic Scleroderma in a Patient with Leg Ulcer
Article information
Abstract
Systemic scleroderma is an autoimmune disease that affects connective tissue in internal organs and the skin with thickening and fibrosis. When afflicting internal organs, the disease leads to reduced quality of life and even morbidity. Meanwhile, systemic scleroderma of the skin is often indicative of the same disease in internal organs. One symptom of systemic scleroderma of the skin is ulcers, mainly reported on fingers and less so on legs. This makes systemic scleroderma difficult to diagnose when patients present with only a leg ulcer. Here we report a case of a leg ulcer in a 79-year-old woman who was ultimately diagnosed with systemic scleroderma.
서 론
전신경화증은 혈관에 손상을 입히고, 결합 조직에 콜라겐이 과다 생성 및 축적되면서 섬유화가 진행되는 자가 면역질환이다[1-4]. 전신경화증의 유병률은 0.007%부터 0.053%까지이며 나라마다 다르나 미국이 유럽, 일본, 대한민국보다 유병률이 더 높으며, 5년 생존율은 74.9%, 10년 생존율은 62.5%로높은 사망률을 보인다[4,5].
전신경화증초기에 레이노현상(Raynauds phenomenon)은 대부분의 환자에게 나타나며, 전신경화증환자 중 약 50%에서 피부궤양이 발생한다. 피부궤양이 심화될 경우에는 감염과 괴사가 발생하고 절단까지 할 수 있다. 피부궤양은 손가락궤양이 많이 보고되었고, 그 외 하지나 다른 부위의 피부궤양은 드물게 보고되었다[1,2]. 또피부와 피하조직을 주로 침범하는 국소성 전신경화증과 다르게, 피부와 피하조직 그리고 내부 장기까지 빠르게 침범하는 전신성전신경화증은 여러 내부장기들에 침범하면 환자들의 삶의 질과 생명을 위협할 수 있다[2,4].
본 연구에서는 외상으로 발생한 하지 피부 창상 치료과정 중에 전신경화증을 진단한 예가 드물어 이를 보고하고자 한다. 연구 및 사진 사용에 대한 서면동의서는 환자로부터 얻었다.
증 례
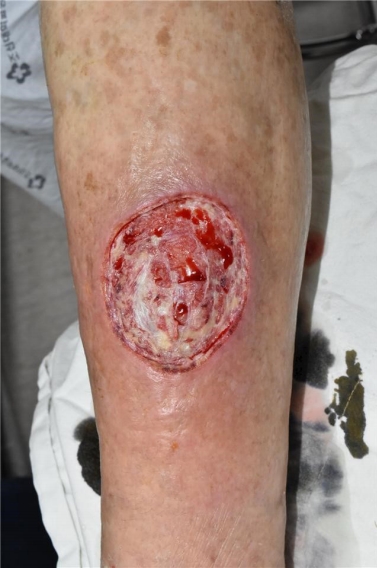
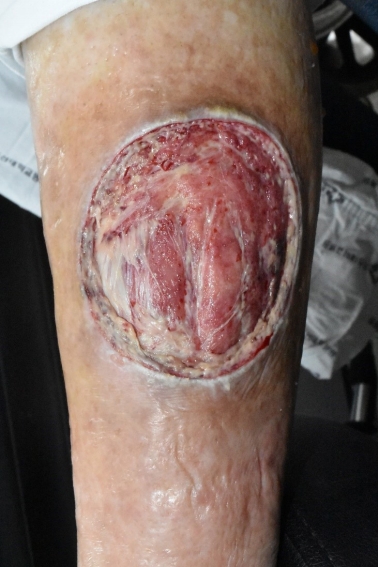
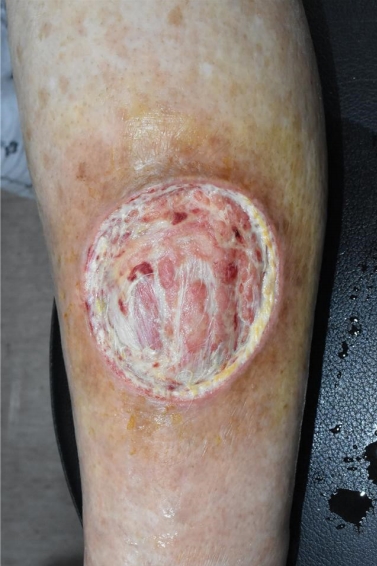
과거에 전신경화증을 진단받지 않은 79세 여자환자가, 내원 한 달 전 탁자에 좌측 정강이를 부딪혀 창상이 발생했다. 다른 병원에서 한 달 동안 치료했으나 호전을 보이지 않아서, 치료 및 피부이식을 위해 본 병원에 입원하였다. 환자는 고혈압 때문에 이뇨제와 혈압 강하제를 복용하고있었고, 당뇨, 흡연력, 음주력은없었다. 또수술을위해입원당시시행한혈액검사, 심전도검사, 단순흉부방사선사진, 폐컴퓨터단층촬영, 심초음파 등의 검사에서 약간의 간질성폐질환과 폐동맥고혈압이 진단되었다. 처음 내원할 때, 하지 피부 창상의 크기는 5×5 cm2이었으며 창상 주위에 발적과 부기가 있었고, 녹농균이 동정되었다(Fig. 1). 입원 후 2주 동안 변연절제술과 드레싱 치료를 지속하였으며(Figs. 2-4), 이후 창상에서 균이 동정되지 않았다. 변연절제술 시행시, 출혈과 통증소견은 다른 피부 창상 환자들과 유사하였으나, 하루 혹은 이틀이 지나면 정상 육아조직이 아닌 하얀 조직들이(Fig. 3) 창상 전체를 덮는 경과가 반복되었다.

The 1st day of hospitalization. An approximately 5×5 cm2-sized ulcer on left lower leg. Swelling and erythema observed around skin ulcer.
The 14th day of hospitalization. Swelling and erythema had been resolved, but the amount of inflamed granulation and fibrosis on the skin ulcer had increased.
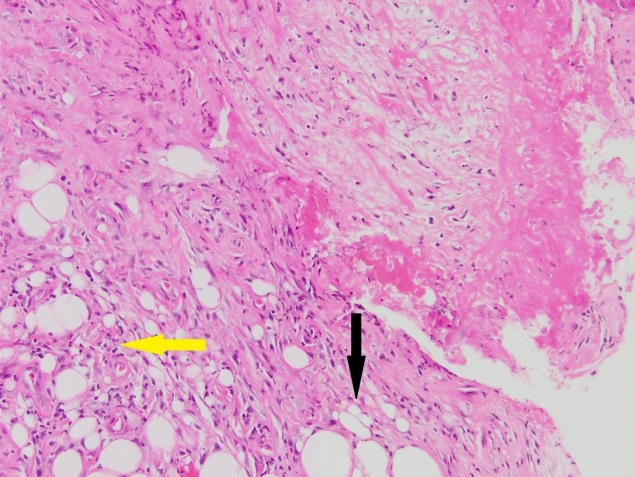
지속적인 치료에도 위와 같은 증상이 반복되어서 하지 창상에서 조직검사를 시행하였다. 입원 시, 신체 검사상 외상으로 발생한 하지 피부창상외 다른 창상은 없었고, 전신적 질환의 가능성을 열어두고 여러 문진을 다시 시행하였다. 그 결과 과거 레이노 현상이 있었으며, 신체검사를 통해 레이노 현상과 손가락 끝 피부가 정상인보다 좀 더 두꺼워진 것을 확인하였다. 추가로 시행한 anti-centromere antibody test에서 양성반응이 나왔고, 조직검사 결과에서는 괴사를 동반한 만성 궤양, 염증을 동반한 육아조직과 섬유증이 나왔다(Fig. 5). 임상증상과 검사결과 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative (ACR/EULAR) criteria에 부합하여 광범위 전신경화증으로 진단하였으며, 내부장기들이 섬유화가 진행되어 있어 기능 저하를 막기 힘든 상태였다. 환자가 호흡곤란 및 통증을 호소하여 류마티스, 신장, 심장, 호흡기 전문의와 상의 후, 증상 조절을 하기 위해 이뇨제와 진통제로 치료하였으나 내부 장기들의 급격한 기능 저하로 입원 후 45일째 다발성 장기부전으로 사망하였다.
고 찰
전신경화증은 발병 원인이 정확히 밝혀지지 않은 드문 질환으로 혈관, 내부 장기, 피부에 콜라겐이 과도하게 생성 및 축적되어 섬유화되는 자가 면역질환이다. 특히 폐, 신장, 심장, 소화 기관과 같은 내부 장기에 침범하게 되면 환자들의 삶의 질을 저하시키고 생명을 위협한다.
전신경화증은 국소성과 전신성으로 나뉘어지며, 과거에 국소성 전신경화증은 주로 안면부 피부가 두꺼워지고 내부 장기를 침범하지 않아서 피부에 국한적으로 영향을 준다고 여겨졌으나, 최근에는 피부 외 다른 내부 장기들에도 영향을 준다고 알려졌다. 또한 폐동맥고 혈압의 높은 유병률을 보이며, 치료하지 않을 경우 5–10년 이내 치명적인 예후가 나타난다. 전신성 전신경화증은 주로 팔꿈치나 무릎 근위부에서 피부가 두꺼워지는 양상이 나타난다. 또, 피부의 침범은 내부 장기 침범과 연관성이 높으며, 특히 심장, 신장, 폐에 침범할 경우 5년 이내 사망할 수 있다. 그러나 병의 초기에 진단하고 치료를 하면 내부장기의 영구적 손상과 사망을 늦출수 있다[4,6].
전신경화증은 ACR/EULAR criteria를 이용하여 진단을 내릴수 있으며[3,7], 레이노 현상은 전신경화증의 초기에 발생할 수 있는 가장 흔한증상이지만, 모든 전신경화증 환자들에게서 발생하지는 않는다[4,6].
전신경화증에서 발생한 피부궤양은 치료가 더디며 재발이 흔하고, 치료가 되지 않고 지속될 경우 감염과 괴사로 진행할 수 있다. 손가락 끝에서 가장 잘 발생하고, 하지나 다른곳의 발생률은 낮다. 피부 궤양은 모든 전신경화증 환자들에게 발생하지 않으며, 발생 시기도 전신경화증을 진단받고 수년 후 발생하기 때문에 발견 당시 병이 진행됐을 수 있다. 위에서 언급한 레이노 현상, 피부궤양, 그리고 진단에 도움이 되는 손발톱 주름, 피부가 두꺼워지는 증상은 전신경화증에서 나타나는 외형증상이지만, 모든 전신경화증 환자들에게 나타나지 않기 때문에 진단이 어렵다[1,3,6,8].
전신경화증 치료는 전신치료와 국소치료로 나눌 수 있으며, 전신 치료로는병의침범부위, 진행상태에따라결정된다. 경증인경우 calcium channel blockers, prostanoids, phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors 등의 혈관확장제를 aspirin과 함께 사용할 수 있으나, beta blocker는 말단 괴사를 악화시킬 수 있다. 중증의 간질성폐질환이나 진행하는 피부병변일 경우 cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate, rituximab 등의 면역 억제제를 사용할 수 있다. 이외 다수의 장기들이 침범될 수 있기 때문에 각 분야의 전문의와 함께 상의하여 치료하는 것을 추천한다[2,6,9,10].
국소치료로는 정상 조직이 손상되지 않게 죽은 조직이나 감염된 조직에 변연절제술을 시행하고, 습윤 드레싱을 유지하며, 감염균이 동정되면 그에 맞는 항생제를 사용한다. 또한 통증 완화를 위해 진통제를 사용하며, 혈관확장제와 고압산소치료도 궤양치료에 도움이 된다[2,4,10,11]. 손끝 피부궤양을 치료하여도 지속적으로 재발하거나 악화되어 활동에 제약이 생기는 경우에는 말초교감신경절제술을 시행해 볼 수 있다. 그러나 치료 후에 다시 재발하거나 병변부위를 절단하는 사례도 있다[10,11]. Calcinosis가 발생하면 통증 조절을 먼저 시행하며, 효과가 없을 경우 수술적 절제, 부피감소술, CO2 laser vaporization 그리고 체외 충격파쇄석술을 시행할 수 있다. 전신경화증 환자에게 발생한 피부궤양은 호전 속도가 느리며, 완전히 치료되기까지 수년의 시간이 걸리기도 한다. 이 중 하지 피부궤양에 대해 보고된 연구는 많지 않고, 연구마다 차이가 있지만 하지 피부궤양 발생 원인의 40%에서 50% 정도가 혈관 침범이라고 한다[1,8,12]. 이를 해결하기 위해서 부분층 피부이식술을 하기 전에 경피경관 혈관성형술, 정맥절제술을 시행하였고, 수술 부위에서 좋은 결과와 빠른 회복속도를 보였다[12].
전신경화증은 발생이 드물며, 예후가 좋지 않은 자가 면역질환이다. 모든 전신경화증 환자들에게 레이노현상, 손발톱주름, 피부가 두꺼워지는 증상, 피부궤양 등이 나타나지는 않으며, 피부궤양이 발생 하였을 경우에는 내부 장기나 혈관까지 침범했을 수도 있다. 하지만 초기에 전신경화증을 진단하고 치료하면 내부 장기의 영구적 손상과 사망을 늦출 수 있다. 전신경화증에서 발생한 피부궤양은 주로 상지나 손가락에서 발생하기 때문에 하지에 발생한 피부궤양에 대한 보고는 찾기 힘들었다. 본 증례는 외상으로 발생한 하지 창상 환자 치료 중에 전신경화증을 진단하게 되었고, 이에 만성창상 치료시, 본증례와 유사한 병변의 환자가 있을 경우 초기에 전신경화증을 감별 및 진단할 수 있게 도움이 되고자 한다.
Notes
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article are reported.